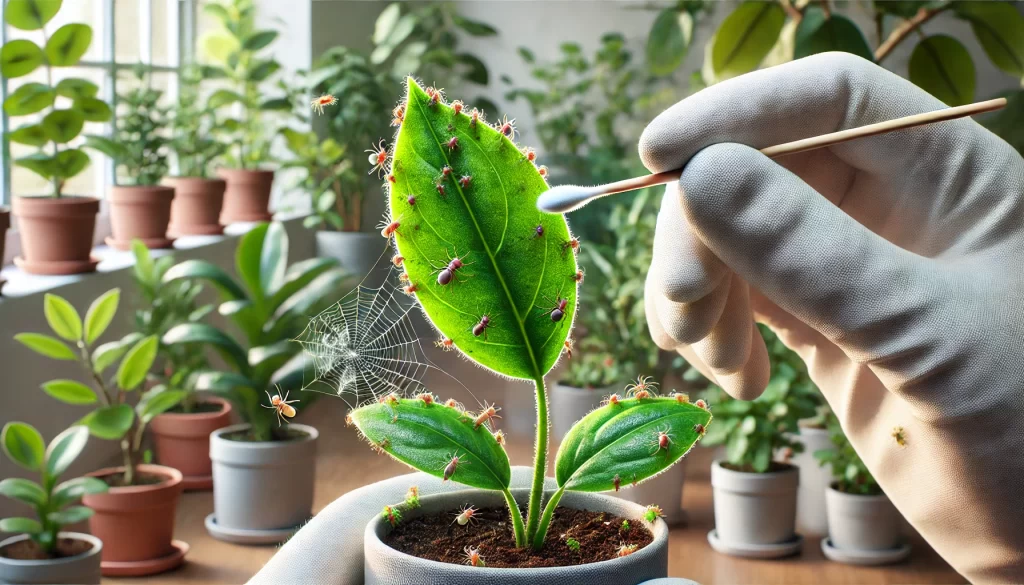
Indoor plants bring beauty and freshness to any home, but they can also attract unwanted pests. These tiny invaders can weaken plants by sucking sap, damaging leaves, and spreading diseases. Identifying and treating pests early is crucial to keeping your indoor plants healthy.
In this guide, we’ll cover the most common indoor plant pests, how to recognize them, and effective treatments to eliminate them without harming your plants.
1. Common Indoor Plant Pests and How to Identify Them
1.1. Aphids
Aphids are small, pear-shaped insects that cluster on new growth, stems, and the undersides of leaves. They feed by sucking sap from plants, causing leaves to curl, yellow, and become distorted.
- Signs of infestation: Sticky honeydew residue, black sooty mold, and stunted plant growth.
- Most affected plants: Herbs, ferns, pothos, and flowering plants like orchids.
1.2. Spider Mites
Spider mites are tiny arachnids that are almost invisible to the naked eye. They thrive in dry environments and leave behind fine webbing on leaves and stems.
- Signs of infestation: Yellow or speckled leaves, webbing between leaves, and dry, curling edges.
- Most affected plants: Fiddle leaf fig, ivy, and palms.
1.3. Mealybugs
Mealybugs appear as small, white, cotton-like clusters on plant stems and leaf joints. They feed on plant juices and weaken the plant over time.
- Signs of infestation: White, waxy residue, sticky leaves, and leaf drop.
- Most affected plants: Succulents, rubber plants, and monstera.
1.4. Fungus Gnats
Fungus gnats are tiny black flies that hover around the soil surface. Their larvae feed on organic matter and plant roots, which can cause root rot in severe cases.
- Signs of infestation: Small black flies near the soil, slow plant growth, and yellowing leaves.
- Most affected plants: Peace lily, pothos, and any plant in moist soil.
1.5. Scale Insects
Scale insects look like small, brown or tan bumps on stems and leaves. They attach themselves to plants and feed on sap, weakening the plant over time.
- Signs of infestation: Brown or yellow spots, sticky residue on leaves, and poor plant health.
- Most affected plants: Orchids, ferns, and citrus trees.
2. How to Get Rid of Indoor Plant Pests
2.1. Manual Removal
For small infestations, manually removing pests can be an effective first step.
- Use a cotton swab dipped in rubbing alcohol to wipe off mealybugs and scale insects.
- Spray plants with water to dislodge aphids and spider mites.
- Prune heavily infested leaves or stems to prevent pests from spreading.
2.2. Natural Remedies
Using organic pest control methods helps protect your plants without introducing harmful chemicals.
- Neem oil spray: Mix 1 teaspoon of neem oil with water and spray on affected areas. Neem oil is effective against aphids, spider mites, and scale.
- Insecticidal soap: A gentle, plant-safe soap solution can suffocate pests. Mix mild dish soap with water and spray onto leaves.
- Diatomaceous earth: Sprinkle food-grade diatomaceous earth on the soil to kill fungus gnat larvae.
2.3. Biological Pest Control
Introducing beneficial insects can help control pest populations naturally.
- Ladybugs: Natural predators of aphids and mealybugs.
- Predatory mites: Feed on spider mites and keep their numbers low.
- Nematodes: Microscopic worms that target fungus gnat larvae in the soil.
2.4. Chemical Treatments (As a Last Resort)
If natural methods fail, chemical insecticides can help eliminate severe infestations. However, they should be used sparingly and according to label instructions.
- Systemic insecticides: Absorbed by the plant and kill pests from the inside.
- Horticultural oils: Smother pests without harming the plant.
3. How to Prevent Pests on Indoor Plants
Prevention is the best defense against plant pests. Here’s how to keep your plants pest-free:
3.1. Inspect New Plants
Before introducing a new plant to your home, check for signs of pests, such as sticky leaves, webbing, or tiny bugs. Quarantine new plants for 1–2 weeks before placing them near others.
3.2. Maintain Proper Plant Care
Healthy plants are more resistant to pests. Follow these plant care tips:
- Avoid overwatering, which can attract fungus gnats and promote mold growth.
- Provide adequate air circulation by spacing plants apart.
- Dust and clean leaves regularly to prevent pests from settling.
3.3. Use Well-Draining Soil
Fungus gnats thrive in damp soil. Ensure your pots have drainage holes and use a soil mix that allows water to drain properly.
3.4. Keep an Eye on Humidity Levels
Spider mites prefer dry conditions, while fungus gnats thrive in humid environments. Adjust humidity based on your plant’s needs to prevent pest problems.
3.5. Rotate Natural Pest Repellents
Spraying plants with neem oil every few weeks or placing cinnamon on the soil can help prevent pests from taking hold.
Final Thoughts
Dealing with indoor plant pests can be frustrating, but with the right approach, you can eliminate infestations and keep your plants healthy. Regular inspections, good plant care, and natural pest control methods are the best ways to prevent and manage these common problems. By staying proactive, your indoor garden will remain lush and thriving year-round.
Critical Observator offers expert tips and guides to make indoor plant care easy, enjoyable, and accessible.