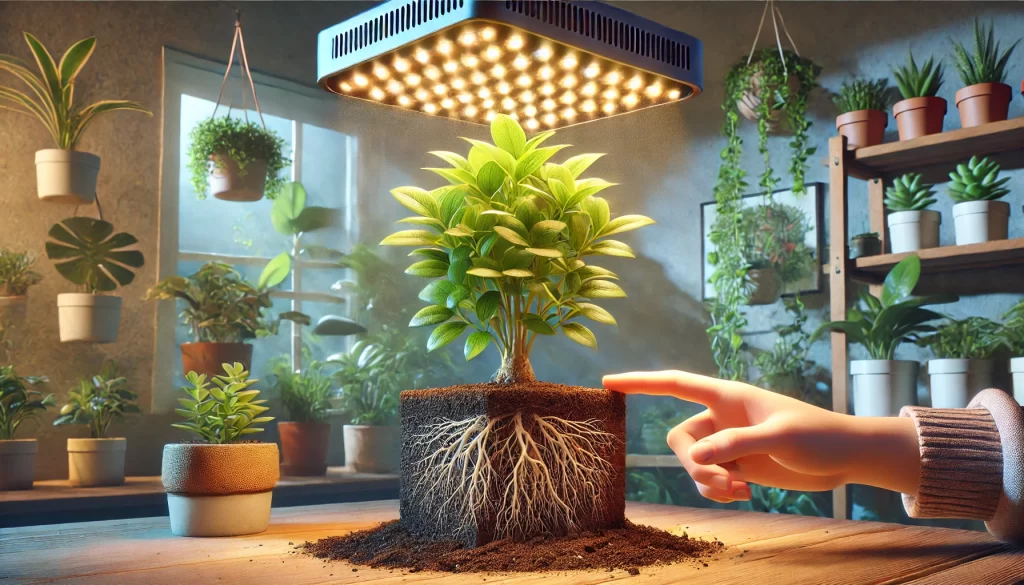
Plants are living organisms that rely on a delicate balance of light, water, and nutrients to thrive. Whether growing indoor houseplants, herbs, or vegetables, understanding how these elements work together is crucial for healthy plant development.
This guide will break down the scientific principles behind plant growth, explaining the role of photosynthesis, hydration, and essential minerals. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to optimize conditions for stronger, greener, and more productive plants.
1. How Plants Use Light for Growth
Light is the primary energy source for plants, enabling photosynthesis, the process that converts sunlight into chemical energy.
1.1. The Role of Photosynthesis
During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) and light energy to produce oxygen and glucose, which fuels growth. This process occurs in chloroplasts, where the pigment chlorophyll captures light energy.
✔ Formula for Photosynthesis:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
1.2. Best Light Conditions for Plants
Different plants require varying levels of light, categorized into:
☀ Full Sun (6–8 hours of direct light) – Tomatoes, peppers, succulents
🌤 Bright, Indirect Light (4–6 hours of filtered light) – Pothos, snake plant, ferns
🌑 Low Light (Minimal natural light exposure) – ZZ plant, peace lily, cast-iron plant
If natural light is insufficient, grow lights provide a solution. Full-spectrum LED grow lights mimic sunlight, promoting healthier growth indoors.
2. The Importance of Water in Plant Growth
Water is essential for nutrient transport, photosynthesis, and cellular structure. It helps dissolve minerals in the soil, allowing roots to absorb and distribute them throughout the plant.
2.1. How Plants Absorb Water
✔ Root Uptake – Water enters the plant through root hairs, moving upward through the xylem.
✔ Transpiration – Water evaporates from leaves, pulling more water upward.
✔ Turgor Pressure – Maintains cell firmness and supports plant structure.
2.2. Signs of Overwatering and Underwatering
💧 Overwatering Symptoms: Yellow leaves, root rot, mold growth
🌿 Underwatering Symptoms: Wilting, dry soil, crispy leaf edges
To prevent these issues, use the finger test—insert a finger into the soil; if it’s dry 1–2 inches down, it’s time to water.
3. Essential Nutrients for Plant Growth
Plants need a mix of macronutrients and micronutrients to thrive.
3.1. The Three Main Macronutrients (N-P-K)
✔ Nitrogen (N) – Encourages leafy, green growth
✔ Phosphorus (P) – Supports root development and flowering
✔ Potassium (K) – Strengthens plant immunity and fruit production
3.2. Secondary and Micronutrients
✔ Calcium (Ca) – Strengthens cell walls
✔ Magnesium (Mg) – Aids in chlorophyll production
✔ Iron (Fe) – Prevents yellowing leaves (chlorosis)
If soil lacks nutrients, use organic compost, liquid fertilizers, or slow-release granules to replenish them.
4. Factors That Affect Plant Growth
✔ Soil Quality – Well-draining, nutrient-rich soil promotes healthy roots.
✔ Humidity – Tropical plants require high humidity, while succulents thrive in dry air.
✔ Temperature – Extreme cold or heat can slow growth or damage plants.
5. How to Optimize Plant Growth
🌞 Provide Adequate Light – Use grow lights for indoor plants lacking sunlight.
💧 Follow a Proper Watering Schedule – Adjust watering based on plant needs.
🌿 Fertilize Wisely – Use organic compost or NPK fertilizers when necessary.
🪴 Prune Regularly – Remove dead leaves to encourage new growth.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the science behind plant growth helps create optimal conditions for healthier plants. By balancing light, water, and nutrients, you can ensure your indoor or outdoor garden thrives year-round.
Critical Observator offers expert tips and guides to make indoor plant care easy, enjoyable, and accessible.